Surgical Insights: Exploring Types and Outcomes of Cavernous Malformation Surgery

Cavernous malformations, also known as cavernous angiomas or cavernomas, are clusters of abnormal blood vessels typically found in the brain and spinal cord. They can cause various neurological symptoms, including seizures, headaches, and hemorrhagic strokes.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat these malformations. Rarely, surgery is performed on an emergency basis following a significant hemorrhage. In other cases, patients have the time to discuss their options with their neurosurgeon to determine the best way to proceed based on their health and preferences.
Before we delve into the different surgical procedures used to treat cavernomas, it helps first to understand what it is and what symptoms it can cause.
What Is a Cavernous Malformation?
Cavernous malformations are clusters of abnormal blood vessels that can form in the brain and spinal cord. They are low-flow vascular lesions with a characteristic “popcorn-like” appearance on MRI scans because of the presence of blood at various stages of degradation.
Although many individuals with cavernous malformations experience no symptoms, these vascular anomalies can cause headaches, seizures, hemorrhages, or neurological deficits. When symptomatic, surgical intervention might be recommended.
Surgeries for Cavernous Malformation
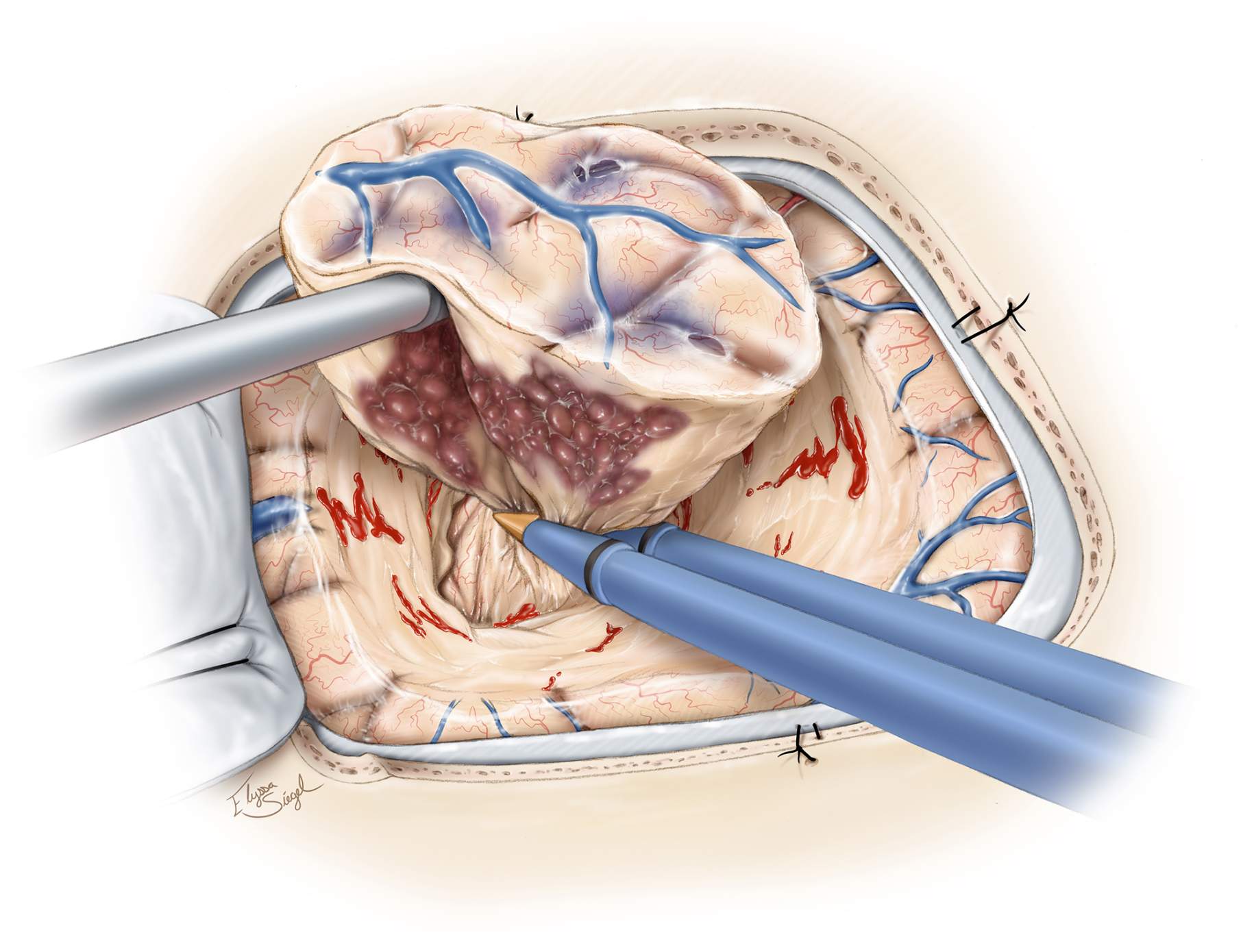
Microsurgical Resection
Microsurgical resection is a delicate surgical technique used to treat various medical conditions, including brain lesions such as cavernous malformations.
It involves a neurosurgeon making a small craniotomy, an opening in the skull, to access the area of the malformation. Under the guidance of a high-powered microscope, the surgeon carefully separates and removes the malformation from the surrounding brain tissue.
The operating microscope used in this procedure gives the surgeon a magnified view of the brain’s intricate structures, allowing for the precise excision of the lesion. This also aids in preserving neurological function by minimizing the risks of damaging critical brain pathways and reducing postoperative complications.
Why should you have your surgery with Dr. Cohen?
Dr. Cohen
- 7,500+ specialized surgeries performed by your chosen surgeon
- More personalized care
- Extensive experience = higher success rate and quicker recovery times
Major Health Centers
- No control over choosing the surgeon caring for you
- One-size-fits-all care
- Less specialization
For more reasons, please click here.
Long-Term Outcomes
The long-term outcomes of microsurgical resection for cavernous malformation are generally favorable, with many patients experiencing immediate relief from or reduction in symptoms and a lower risk of recurrent bleeding. However, it is worth noting that individual results still vary from individual to individual.
Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the patient’s neurological status and detect potential recurrences early on. Imaging studies may be repeated periodically to ensure the malformation has been completely resected and to assess for any new developments.
Post-Procedure Recovery
After the surgery, patients will spend time in an intensive care unit for close monitoring before moving to a regular ward. The recovery process includes a combination of rest, rehabilitation, and follow-up assessments.
Patients should generally expect gradual improvement in their condition, but the speed and extent of recovery can vary depending on the individual and the complexity of the surgery.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a newer, non-invasive medical procedure using focused beams of high-energy radiation to treat abnormalities, tumors, and other conditions within the brain and body.
Unlike traditional surgery, SRS does not require any incisions. Instead, it directs highly precise, concentrated radiation doses to specific areas, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
SRS offers a less invasive treatment option for patients with cavernous malformations, especially those that are surgically inaccessible. It’s also best for patients who are not ideal surgical candidates due to various risks.
The focused radiation creates scarring and eventually shrinks the malformation, reducing the risk of bleeding and associated symptoms. It is important to note that the advantage of SRS over surgery for lesions that are accessible surgically is controversial.
Preparing for SRS
Before undergoing stereotactic radiosurgery, you will undergo a thorough evaluation, including imaging tests and possibly a neurological assessment, to help tailor the treatment. Doctors will provide specific instructions on how to prepare, such as restrictions on eating and drinking and guidelines on medication use.
Possible Side Effects and Recovery
Stereotactic radiosurgery takes about one to four hours and does not require incisions, so most patients experience minimal immediate side effects. They can also go home the same day and resume normal activities the following day.
However, potential delayed side effects like fatigue, headaches, or swelling at the treatment site can occur. Follow-up imaging is essential to monitor the efficacy of the procedure and any late-onset side effects.
What to expect after cavernoma surgery?
After cavernoma surgery, recovery experiences vary depending on the cavernoma’s size and location. Initially, patients may experience headaches, fatigue, or temporary weakness as the brain heals. Hospital stays typically last a few days, followed by several weeks of rest and sometimes rehabilitation.
Physical, occupational, or speech therapy may be recommended to regain strength and coordination. Some people notice an improvement in symptoms like seizures or vision problems, while others may take longer to recover fully. Regular follow-up scans help ensure the cavernoma has been completely removed and no new issues develop. Patience and consistent care are key to a successful recovery.
Cavernous Malformation Brain Surgery Success Rate and Risks
Success in cavernous malformation surgery typically refers to the complete resection of the malformation, reduction or cessation of symptoms, and the prevention of future hemorrhages or seizures.
The success rate for cavernoma surgeries is generally high, with over 80% of patients experiencing improvements in symptoms following surgery.
Many patients also experience an improved quality of life post-surgery, with reduced seizure activity and lowered risk for recurrent bleeding. While approximately 5% of patients experience new worsening symptoms immediately after the operation, most recover over time.
Moreover, surgery performed by a skilled and experienced surgeon makes death resulting from surgery extremely unlikely. Mortality rates in cases of cavernous malformations in critical areas of the brain like the brainstem are less than 1% to 2%.
Ultimately, the expertise of your chosen neurosurgeon can significantly improve the outcome of your cavernous malformation brain surgery. This is why it’s crucial that you work with a skilled and experienced surgeon. He or she wiill be able to address anticipated and unexpected challenges presented by the malformation and improve the likelihood of a successful surgery with minimal risks.
Key Takeaways
Cavernous malformations are a type of vascular anomaly that can cause neurological symptoms such as seizures, headaches, and hemorrhagic strokes.
Surgery is one of the preferred treatment options available for patients with symptomatic cavernomas, with different procedures presenting different advantages and potential risks.
Deciding which cavernous malformation surgery to undergo should be made in consultation with a qualified neurosurgeon. It’s also a good idea to request a second opinion from neurosurgeons with experience handling complex brain surgeries.
Seeking professional advice can help you find the surgery that allows you to achieve favorable cavernous malformation surgery outcomes and, most importantly, enjoy an improved quality of life.